Links are one of the primary ways Google and other search engines understand and rank websites. Crawlers and bots follow links from external sites to your web property and then trace the internal links on your site, measuring the “flow” of ranking signals and attributing them to sites accordingly.
“Link flow goes by many names,” said Jonathan Epstein, CEO of Brewco, at SMX Next. “Some people call it link juice. Some people call it PageRank. In the broadest terms, link flows are a measurement of how important your pages are relative to other pages out there on the Internet.”
According to Epstein, two main signals go into calculating PageRank: the types of sites linking to your property and what your internal link structure looks like.
“The first is: What are the other sites that are linking to each of your pages?” he said. “How many are there? How big are they? How authoritative are they? And then secondly, it looks at how are you linking your pages to each other.”
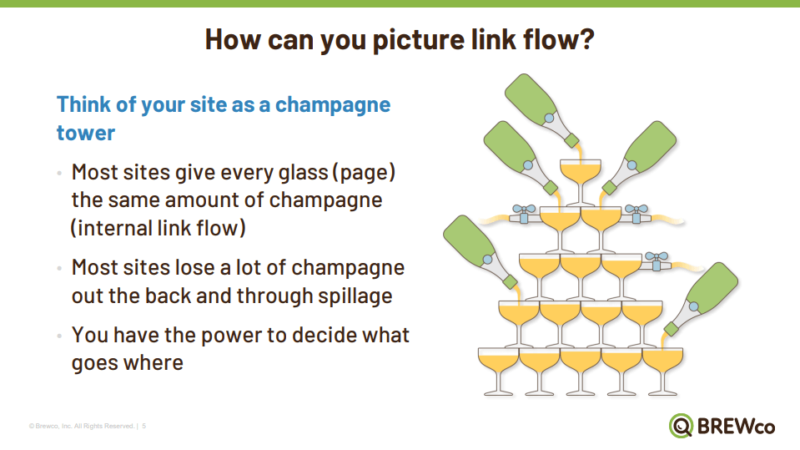
Most marketers tend to focus a lot on gathering backlinks to improve their properties while neglecting to optimize internal links on their site. But, to get the most out of all the sites linking to your pages, marketers should make sure their internal link structure is well-optimized.
Here are three ways Epstein recommends marketers best optimize their sites with internal linking.
Optimize distribution of link flow
“How do you stop pushing link flow to less important pages and push it to the more important ones?” Epstein asked. “Start by removing extraneous links that don’t need to be there.”
These extraneous links are often copied on multiple pages and featured near the top of pages, such as job openings, report downloads, or company mission statements. While these are important pieces of information for visitors on the site, there’s a good chance they won’t be the most SEO-friendly pages.
To address these issues, Epstein suggests marketers remove these links where possible, especially if they’re repeated often. Then, place links to pages that are better optimized for search.
“Add links to the pages you want to push up based on their importance . . . If you can do this systematically across the pages of your site, you can start to push up internal link flow to the pages you want to have it and limit it to the pages that don’t need it because they’re not important for search.”
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on. See terms.
Reduce link flow loss
While optimizing link flow is important, marketers need to simultaneously review instances of ranking loss through links. This occurs most often when sites link to pages that aren’t search-friendly, such as internal search result pages or old tag pages that don’t receive traffic.
There are many instances where linking to these less important pages is necessary for site operations, so removing them isn’t always an option. Instead, Epstein recommends marketers compensate for these links’ PageRank loss by always linking back from every internal page you link to.
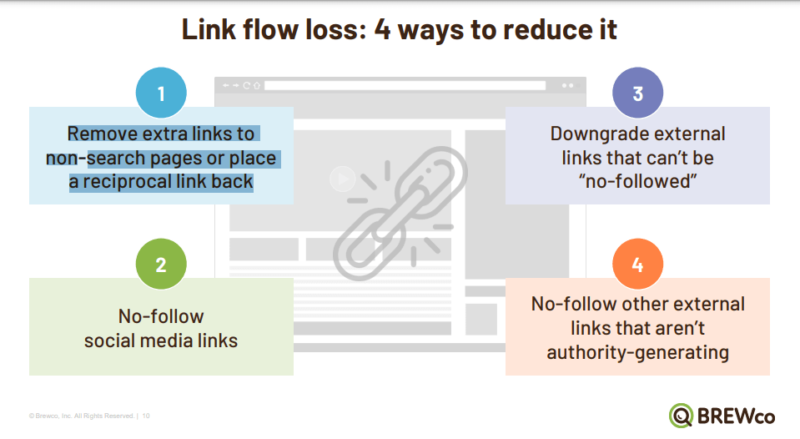
Marketers should also consider how they’re using nofollow links in the site content. Though there’s some debate as to how much impact these attributes have on the overall ranking, Epstein believes strategic nofollow tag use can effectively reduce link flow loss.
“We like to use the nofollow tag,” he said. “We see a lot of people losing link flow to social media accounts. We see them losing it to customer login sites and help sites and partner sites. If you do have to have followed links that go out to external sites, consider downgrading them using lower point sizes, putting them further down on the page, or adding other links to the page.”
Eliminate penalty factors
“Penalty factors are things that your pages do that might make them look like spam pages,” Epstein said.
One of the most common penalty factors related to page ranking is duplicate content. It tells search engines that your site has poor content quality. Too many internal links to content with potential penalty factors could end up harming your site rankings.
“Apart from your header and footer, your pages shouldn’t share ideally more than about half of the words with each other,” said Epstein. “But we see tons of pages where a page will share 90% of its words with another page on the site.
Marketers should also avoid linking to too many pieces of “thin” content on their sites. These are pages with very low word counts that are set up to be informative pieces but give little information.
“When you’re sending out link flow to other sites, be careful with how they’re positioned,” said Epstein. “Too many unreciprocated, followed editorial links make it look like you’re an advertorial site even though you’re not.”
Building a high-quality, relevant backlink profile is important, but optimizing your internal linking structure and eliminating risk factors is vital to reaping the most benefits from ranking signals.
Watch the full SMX Next presentation here (free registration required).
New on Search Engine Land